Hair Health and Anatomy – Canterbury Hair & Scalp Clinic
Anatomy and Structure
Hair is made up of three layers: the cuticle, the cortex and the medulla.
The Cortex
The cortex makes up the main bulk of the hair and helps determine the texture – dry, damaged, low water content. Melanin the colour pigment is present in the cortex and determines the colour of the hair. No melanin present and the hair will appear grey but will actually be colourless.
Hair is a protein made up of amino acids, that’s why it’s important to make sure you are eating enough protein for optimal hair health and it’s better digested earlier in the day.

The Cuticle
The function of the cuticle is to protect and hold together the hair. It consists of roughly 5-10 overlapping translucent keratin scales which are hard and protect the hair from losing moisture. Our natural oil or sebum helps to coat the hair and stop moisture from escaping. It can also stop moisture from being able to get into the hair along with other oil.

The Medulla
Not all hairs contain a medullla, this depends on the thickness or diameter. The medulla if present is the central part.
Texture


Hair Properties
Hair is hygroscopic which means it can absorb water from the atmosphere, this is why hair can go frizzy if it is dry inside. In a really dry atmosphere, water can be pulled out of the hair into the atmosphere. Put some oil or serum on your hair after you have washed it to help lock the moisture inside.
Elasticity – Cross bonds enable hair to stretch to a third of it’s length and return back to normal, providing it’s cuticles are intact and it’s reasonably healthy. Hair that does not return back to normal or breaks is lacking protein and a treatment conditioner with protein fibres in will help to fill in some of the gaps. A leave in conditioner will also help with moisture.
Static electricity – hair has the ability to conduct static electricity. Dry hair that has a low water content becomes static or ‘fly away’. Leave in conditioner will help with the moisture content.
Porosity – Hair can absorb liquids into it’s cortex and it’s porosity depends on the condition of the cuticles, if they are damaged then the hair will lose moisture and this could lead to breakage. Hair can react differently to colour if it has a low water content, it can grab the colour and go too dark or it can also not take the colour and wash out really quickly.
Hair Growth Cycle
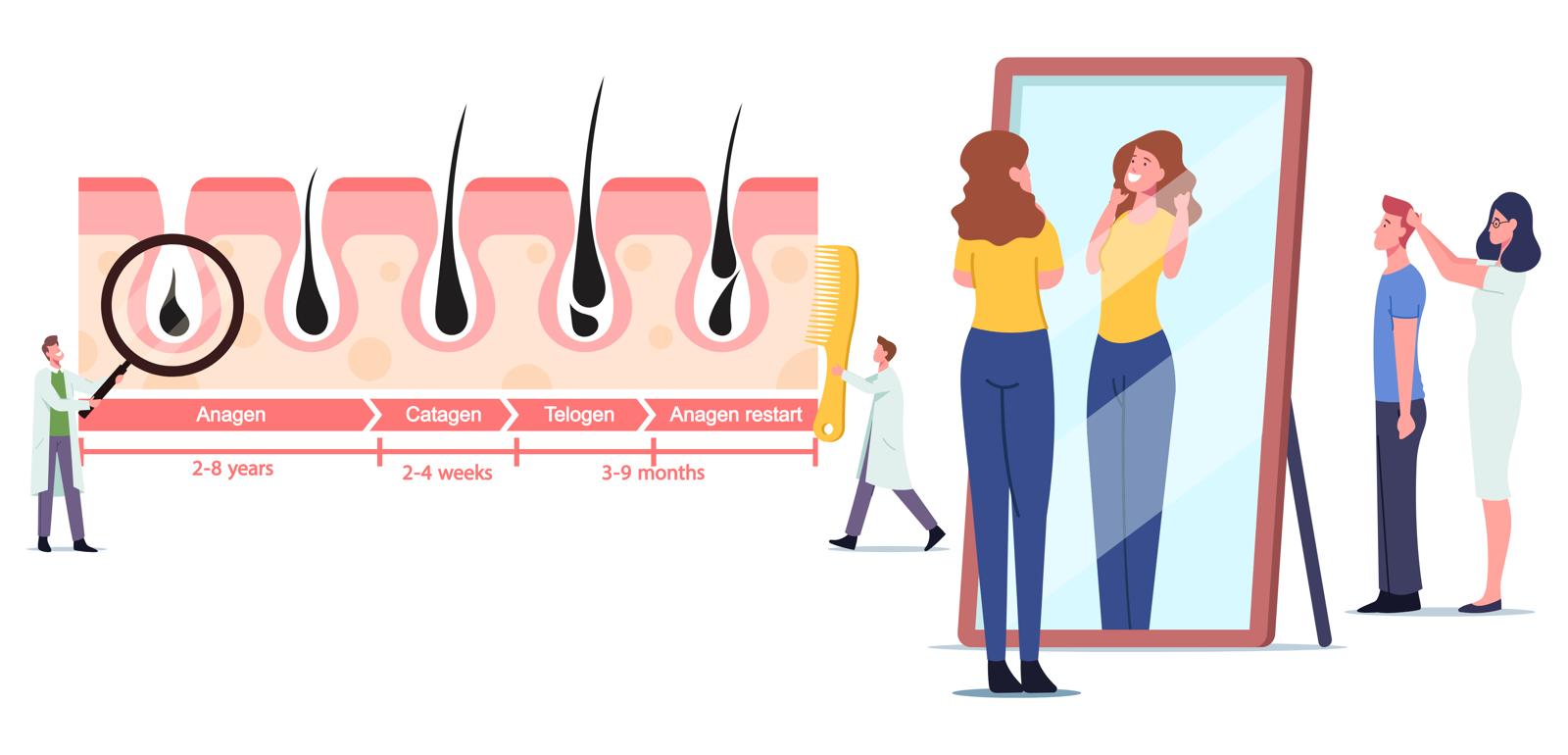
The hair growth cycle consists of three distinct stages or phases – anagen, catagen and telogen.
The anagen stage is the growing stage and lasts between 2-7 years where the hair is growing out of the scalp and keratinising. Hair is made up of dead keratin cells which is why it doesn’t hurt when we cut them.
The second stage is the catagen stage, also known as the transitional phase where the hair is cut off from the blood supply and transitions into the telogen stage. This is the shortest stage and lasts around 2 weeks or 10 days.
The last stage is the telogen stage or the resting stage. Here the hair is just sitting in the hair follicle, still keratinising but there is no longer any melanin or colour present in the root as it is no longer being fed with blood. This stage last between 2 and 4 months where the hair follicle is simply resting and then the hair is shed. When the hair exits it’s another stage or phase called exogen – the end of the telogen phase and usually a new anagen hair is already underway.
Racial Types of Hair



Types of hair on the human body


Damage/trauma



